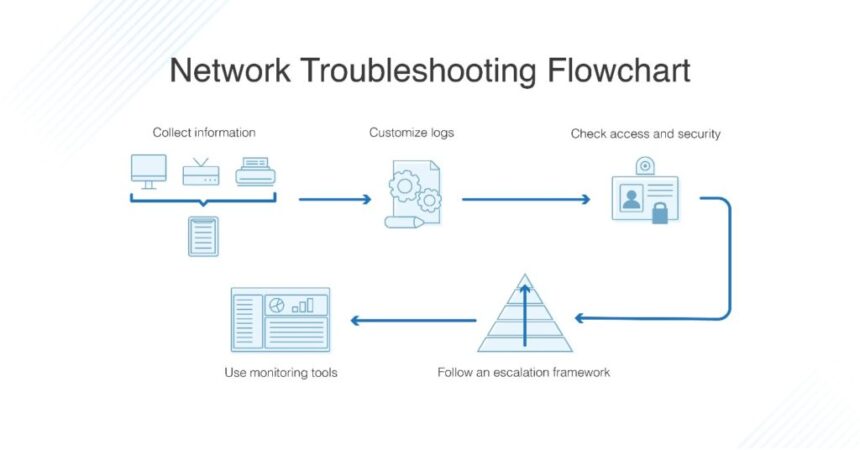
Have you ever faced a sudden network outage or slow connection during an important task? Network issues can be incredibly frustrating, significantly when they interrupt crucial work. These problems often arise from malfunctioning devices, poor connections, or outdated equipment.
Understanding network components is critical to troubleshooting connectivity problems. These elements are crucial in maintaining smooth communication, whether it’s a router or wireless access point. Fortunately, most of these problems have quite a straightforward solution. Take a look.
Connectivity Drops and Slow Speeds
One of the most common issues users experience is frequent connectivity drops or slow speeds. Faulty cables can cause improper placement of routers or interference from other devices. Wireless signals, for instance, may weaken if the router is placed too far from the device. Resolving this involves repositioning the equipment and ensuring proper cable connections. Another solution is checking for interference from nearby electronics, which can disturb wireless signals.
Hardware Failures
Hardware failures in network equipment can lead to complete outages. Routers, switches, and modems are prone to wear and tear over time. The internal circuitry of these devices may deteriorate, affecting their performance. A simple reboot or reset might temporarily solve the issue, but replacing outdated hardware is often the most effective long-term fix. Keeping equipment updated ensures better performance and fewer failures.
Configuration Errors
Incorrect configuration is another frequent issue that can disrupt network performance. This often happens when users attempt to manually change settings without clearly understanding how these changes affect the network. Misconfigurations in routers, IP addresses, or firewalls can prevent devices from communicating correctly. To avoid this, it’s essential to regularly update firmware and consult the documentation provided with the equipment. If the problem persists, resetting the device to its default settings might restore functionality.
IP Address Conflicts
They occur when two devices on the same network are assigned to a similar address. This can result in one or both devices losing connectivity. In home or small office environments, this often happens when Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is not configured correctly. To resolve this, check the DHCP settings on your router and ensure it assigns unique IP addresses to each connected device. Manually assigning static IP addresses can also prevent future conflicts.
Weak Wi-Fi Signals
Weak Wi-Fi signals can make it difficult for devices to connect reliably to the network. This is often due to interference, distance, or barriers such as walls. Moving the router to a more central location can help boost signal strength. Upgrading to a router with a more robust signal range or using range extenders can improve overall coverage. If interference is suspected, switching to a different channel on the router may reduce interruptions.
Firmware and Software Issues
Outdated firmware and software in networking equipment can lead to compatibility problems or security vulnerabilities. Most network equipment manufacturers release regular updates to address these issues. Keeping devices updated with the latest firmware ensures they function optimally and remain secure from threats. Checking for updates periodically is a good practice that helps avoid performance slowdowns or security breaches.
Overloaded Networks
Network congestion happens when too many devices try to use the same bandwidth at once. This can cause slowdowns or connectivity issues, particularly in busy offices or homes with multiple users streaming. Users can set up a guest network for visitors to reduce congestion or upgrade to a higher-bandwidth plan. Limiting the number of devices connected simultaneously can also help alleviate the problem.
Addressing common problems with network components can drastically improve the performance and reliability of your internet connection. Users can prevent future disruptions by keeping equipment updated and resolving disputes. The key is staying proactive and ensuring all the network elements function optimally.